과전만 요추(Hyperlordosis posture)에 대한 조심해야할 운동 접근(Clnical approach)
안녕하세요.
척추안정화 연구소 통합 체형 전문가 과정 (PIT) 과 기능적 움직임 패턴 과정(FST)강사이자
Bodymove운동센터 대표 마혁빈 입니다.
오늘은 과전만(Hyper Lordosis) 요추자세에 관한 조심해야할 운동접근법이란
( Functional Training Approach for Hyperlordosis posture) 주제로 글을 남겨볼까합니다.
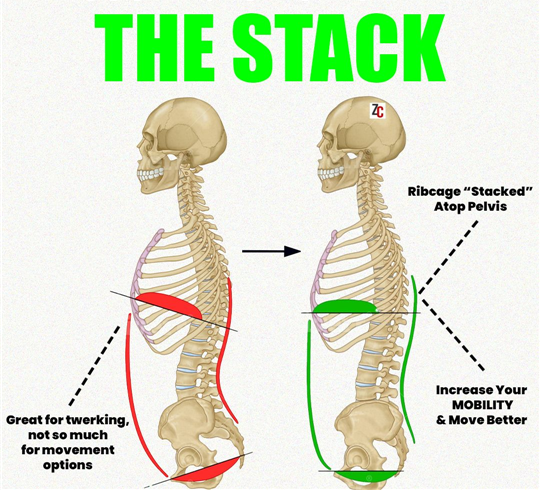
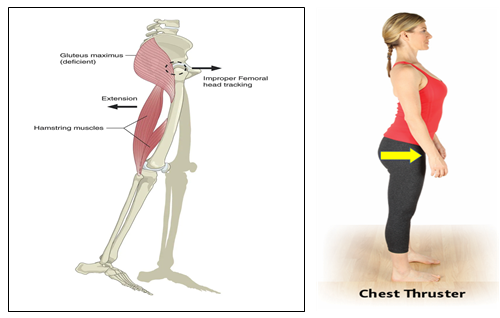
일반적으로 과신전자세에 놓여진 사람들은 척추기립근의 과도한 활동으로
허리만곡이 증가되어 있고,전면부 갈비뼈가 위쪽으로 들러올려져있는
상태의(Open Scissor) 모습을 많이 관찰할 수 있습니다.
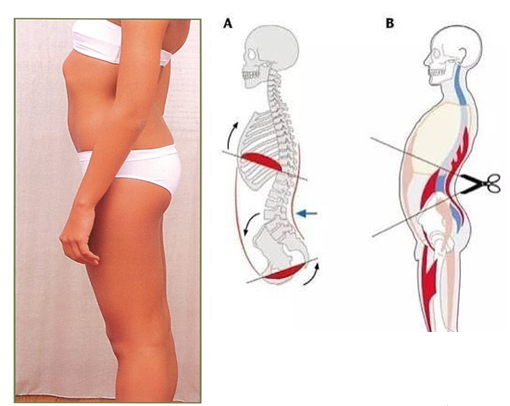
이러한 체형을 가지고 있는 사람들은 앞쪽 복부가 과도하게 신장되어져있어서
횡경막의 수축과 이완을 통해 체간의 안정화에 관여하는 복횡근(Transverse Abdominis)과
허리주변부위 심부근육의 활성화가 잘 이루어 지지않게 됩니다.
이러한 근육들의 비활성화는 척추와 상체의 하중을 지지하는데
필요한 복부내압( Intra Abdominal Pressure:IAP)을
적절하게 생성할수없다라고 많은 연구결과를 통해 언급되고있습니다.

우리가 무게를 드는 작업을 하거나 중량을 이용하는 운동수행시 복강내압(IAP)을
유지하지 못하면 위그림처럼 어깨 관절의 굴곡이나 외전시에 허리가 과도하게
젖혀지거나 불안정해져서 척추에 많은 스트레스를 줄수가 있게됩니다.
또한 , 정상적인 사람은 활동하는 동안 복횡근이 자세유지근으로(Tonic activation)
작용하는 방면에 과전만 요추자세를 가진 환자들은 자세유지근의 활동(Tonic M.)보다는
위상성 근육활동(phasic activation을) 일으킵니다.
비 정상적인 자세나 체형의 문제를 가지는 사람의 경우에는 신체의 에너지소모를 좀 더 증가시켜
신체의 피로도를 가중시킬 수 있는 위상성근육의(Phasic Muscle Activation)활동을 증가시킬 수 있는데,
복횡근의 약증과 횡경막의 활동부재로 인해 복강내압이(IAP) 약해지면 척추를 기립할 수 있는 능력이 소실되기
시작하면서 위상성근육인 척추기립근(Erector Spinae M.)이 과도하게 작용하여
허리의 과전만(Hyper Lordosis)을 만들어 낼수가있습니다.
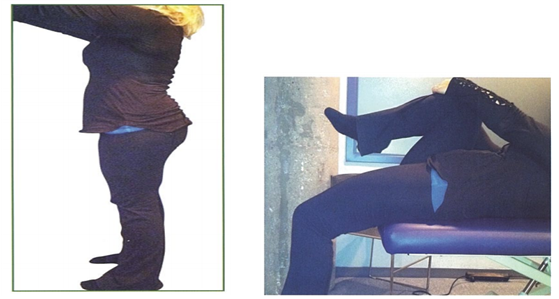
실제적으로 임상에 계시는 선생님들이 요추과전만(Hyper lordosis)을 가진 환자들을
대상으로 토마스 테스트를 검사해보면 장요근이 짧아져있는 임상케이스의 환자는
거의 보기가 힘듭니다.
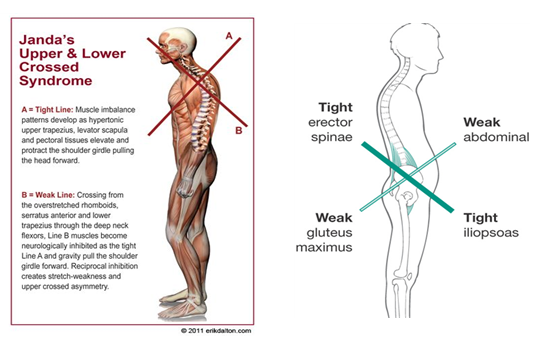
운동치료의 선구자이신 얀다선생님의 하지 교차증후군(Lower Cross Syndrome)에서는
분명 요추과전만자세는 장요근(Iliopsoas M.)이 타이트하거나 과활성화 단축 소견등의
반응이 나와야 하는데 실제 임상케이스에서는 양성반응(고관절이 테이블위에 떠서 단축되어있는 반응)이
나오지 않는 경우가 거의 대부분이고 실제로는 장요근은 약해져있고 신장되서 늘어난 케이스가 대부분이죠.
이 부분은 요추과전만자세가 실제로 함스트링이 늘어나 있지않고 SLR검사시
가동성 제한이 많이 있는 경우와 비슷한 경우라고 언급해드릴수가 있습니다.
이 부분은 다음에 자세하게 언급해드리겠습니다.(Neurological Tightness Myth)
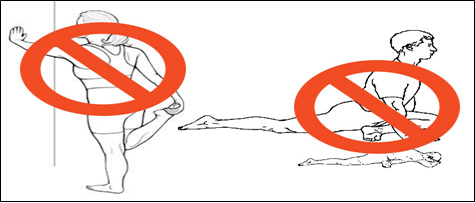
이런 과전만체형을(Hyper Lordosis Posture) 가진 사람들의 경우에
우리가 일반적으로 고관절 굴곡근(Hip Flexor)이자 허리근육인 장요근의 길이와 긴장도를
확인하는 검사인 토마스테스트(Thomas Test)를 실행하고
아래 그림에서처럼 장요근 스트레칭을 마치 루틴운동처럼 많이 실행하곤 하는데요.

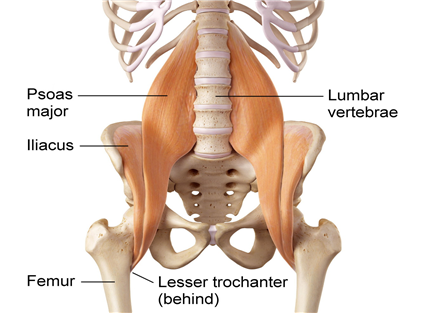
다들 아시겠지만 장요근은 대요근(Psoas Major M.)과 장골근(Iliacus M.)의
두가지 근육이 합쳐져서 넙다리뼈 (Femur)의 작은돌기(Lesser Trochanter)에
부착되어서 이루어진 근육입니다.
이 근육은 척추에서 기시하여 척추안정화근육으로도 작용하고(Hu.2011)
고관절절구내에서( Femur Acetabular) 대퇴골두(Femoral Head)의 중심화를
유지하는데 도움을 준다라고 얘기하고 있습니다.(Gibbons.2005)
국내에 교정운동 솔루션이란 서적으로 많이 알려진 에반오사르(Evan Osar)선생님께서
2019년도에 국내에 방문하셨을 때 국내호스팅을 담당했었는데요.

그때 에반 오사르 선생님께서 얘기하셨던 내용중 하나가 장요근의 단축(Tightness)소견보다는 약해지고
늘어나 문제가 생기는 원인이 많다라는게 상당히 인상깊었던 기억이 있었습니다.
우리가 알고있는 장요근에 대한 미신적인부분과 운동적인스트레칭이 임상적으로
맞지않는 부분에 대한 내용으로요.
실제 에반오사fm선생님의 서적과 관련 연구에서는 코어와 엉덩관절의 기능부전을가진 사람을 도수근력검사를
했을 때 장요근의 약증을 볼수있었고,(2012,Osar)이로 인해 척추 기립근의 과사용과
엉덩관절 굽힘근(Hip Flexor) 으로 작용하는 넙다리 곧은근(Rectus Femoris)과
넙다리근막긴장근(Tensor Facia latae) 의 과사용(Hyper Activity)을 만든다라고 언급하면서
장요근의 비활성화또는 약화는 코어의 자세지지능력과 엉덩관절 조절능력의 소실에
크게 영향을 준다라고 얘기하고있습니다.(2014,Osar)
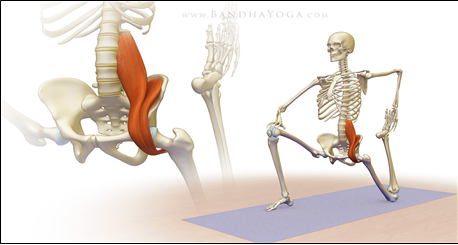
만약에 이러한 자세조절과 체형문제에 관여하여 고관절의 중심화와 체간 코어의 안정화에
도움을 주는 장요근(Iliop Soas M.)을 단순하게 위의 그림에서처럼 장요근 스트레칭이라는
단순한 운동을 적용하게 된다면 많은 효과를 보지못하고 오히려 더 내원하시는
고객이나 환자분들에게 더 안좋은 악영향을 끼칠수가 있습니다.
이러한 장요근 스트레칭에 가장 조심해야할 대표적인예 중 하나로
염발음성고관절 충돌증후군(Snapping Hip Syndrome)과 이에 연관된
대퇴골두 전방활주 증후군(Femural Head Anterior Gliding Syndrome)등을
예로들수가 있습니다.
염발음성 고관절 증후군(Inter Snapping Hip Syndrome)은 일반적으로
세가지 타입을 얘기합니다.
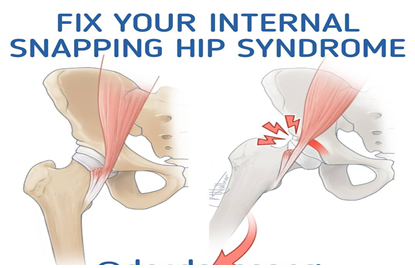
첫 번째로
내측 염발음성 고관절 증후군(Internal Snapping Hip)은 대요근(Psoas Major M.)과
장골근(Iliacus M.)의 힘줄이 골반과 고관절 전면부의 엉덩두덩융기
(장치골 융기-Iliopectineal Eminence) 라는 튀어나오는 구조물과
부딛혀서 나는 고관절의 통증과 염발음을 얘기할 수 있고,
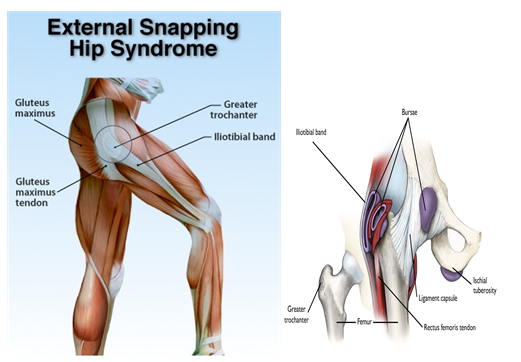
두 번째로
외측 염발음성 고관절 증후군(External Snapping Hip)은 고관절의 염발음이
외측에서 나오는 것으로 고관절의 굴곡(Flexion)-신전(Extension) 시에
대퇴근막장근(TFL)-과 장경인대(ITB)가 고관절의 대전자(Greater Trochanter)와
마찰이 생기면서충돌증후군을 얘기할 수 있습니다.
마지막 세 번째는
Intra-Articular타입으로 고관절주변의 관절와순(Labrum) 또는
연골자체의 구조적 부상(Cartilage Injury)으로 생기는 타입이라
정형외과적인 처치가 필요한 타입입니다.
이러한 내부적인 문제와 체형적인 불균형으로 인해 아래 그림에서처럼 대퇴골두가
전방으로 활주하게 되면서 나오는 대퇴-비구 충돌중후군(FAI-Femoralacetabular Impingement Syndrome)까지 문제가 생길수 있습니다.(대퇴전방활주 증후군-Femur Anterior Gliding Syndrome)
두가지 경우 다 대퇴전면부 내.외측의 관절의 중심화가 깨져있어서
관절 주변조직인대나 캡슐,연골의 불안정성(Instability)과 근육과 힘줄의
약증(Weakness)을 동반하고 있는데 만약 고관절과 골반대의 앞쪽부분을
과도하게 신장시키거나 늘리게되는 스트레칭을 하게 된다면 고관절 전면(Anterior Part)과
주변부 조직손상 이로인한 위험요소는 당연하게 높아지기 때문입니다.
기능적인 검사나 평가를 통한 임상적인 중재요소로 적절한 운동처방이 들어가는 것은 상당히 중요합니다.
인류의 문명과 과학이 발달할수록 수많은 근골격계관련해서도 많은 최신연구들과 임상사례들을 통한
더나은 운동적용방법들과 기법들이 많이 쏟아져나오고있기 때문에 스스로 평가하고
검사했던부분을 바탕으로 접근해보시길 추천합니다.
References
1.Yamamoto Y, Hamada Y, Ide T, Usui I. Arthroscopic surgery to treat intra-articular type snapping hip. Arthroscopy. 2005;21(9):1120-5.
People who pop, click, or snap their hips during particular movements have snapping hip syndrome, also known as coxa saltans or dancer’s hip. Some people make an audible click when they bend at the hip. For other people, hip snapping can be seen, and their hip muscles visibly shudder with certain movements. Still others may feel a popping or catching in their hip joint.
Why does hip snapping occur? This page reviews the three types of snapping hip and their underlying causes. While often harmless, these conditions can sometimes lead to joint damage and pain.
1. Internal Snapping Hip (at the Front of the Hip)
The first type of snapping hip occurs when a tendon slides over protruding bony structures at the front of the hip joint, creating tension and then releasing with a “snap.”
Internal hip snapping is typically caused when either:
•The iliopsoas tendon, which connects two inner hip muscles to the femur (thighbone), moves over a protrusion of the pelvic bone called the iliopectineal eminence.
•The rectus femoris, commonly called a quadriceps muscle, moves over the rounded femoral head, commonly known as the “ball” of the hip’s ball-and-socket joint.
Both the iliopsoas tendon and rectus femoris are commonly called hip flexors.
People with internal snapping hip syndrome may experience:
•Hip popping when running; when the hip is extended from a flexed position of more than 90 degrees, such as when rising from a seated position; or when the hip rotates the leg away from the body
•Hip popping accompanied by a sharp, sudden pain at the front of the hip, deep within the groin
•Pain that worsens with activity, as repeated irritation causes the tendon to become inflamed.
•Gradual onset of painful symptoms—the pain may have begun as a mild annoyance and worsened over weeks or months.
Internal snapping hip is the most common type of snapping hip. It is associated with painful inflammation of a bursa located at the front of the hip joint. This inflammation is called iliopsoas bursitis.
External snapping hip is caused when either:
•The iliotibial band (IT band) slides over a rounded protrusion of the femur (thighbone) called the greater trochanter. The IT band is a wide strip of fibrous tissue that extends down the outside of the upper leg, from the pelvis to below the knee.
•The gluteus maximus muscle slides over the greater trochanter.
External snapping may be a sign that the iliotibial band or gluteus maximus is tight.
People with external snapping hip syndrome may notice:
•The snapping typically occurs during hip flexion and extension, such as when running and climbing stairs. Hip snapping may also be noticeable when playing golf or carrying a heavy load, such as groceries or a heavy backpack.
•Hip popping is accompanied by sharp, sudden pain felt at the outside of the hip.
•The hip feels like it is about to pop out its socket when snapping (it is not).
•Pain that worsens with activity, as repeated irritation causes the tendon to become inflamed.
•The popping hip can often be seen as the IT band or gluteus muscle snaps and causes the overlaying skin to shudder.
•Painful symptoms develop gradually; the pain may begin as a mild annoyance and worsen over weeks or months.
External snapping hip syndrome is often associated with painful tenderness at the outside of the hip, which suggests the athlete may have a type of hip bursitis called trochanteric bursitis.
This syndrome is also associated with a tight IT band, sometimes called IT band syndrome.
3. Snapping Hip Due to Cartilage Injury
A problem within the hip joint itself can cause this third type of snapping hip. For example, a snapping hip may be caused by:
•An acetabular labral tear is an injury to the tough, flexible cartilage that rings the hip socket, like a gasket. A tear can cause a snapping sensation as well as pain in the groin area. One study found acetabular tears accounted for 80% of intra-articular snapping hip cases.1
See Diagnosing a Hip Labral Tear
•An injury to the articular cartilage, which covers bones' surfaces where they articulate, or meet up with one another. This cartilage reduces friction between the bones at the joint, and it can be damaged suddenly from a traumatic injury or over time from arthritis.
•Loose bodies of material in the hip that interrupt the joint’s normal biomechanics and cause a catching or snapping sensation. For example, following a trauma, a fragment of soft tissue or bone can break away and get trapped between the hip’s ball and socket.
Snapping hip due to a cartilage injury may develop suddenly, and may be caused by a fall or other trauma. It is often accompanied by a catching sensation and/or a limited range of motion in the hip.
People who have snapping hip syndrome with painful symptoms should consult a physician. A medical professional can give an accurate diagnosis and help develop a treatment plan to alleviate pain and minimize possible future joint damage.
'근골격계질환 공부끄적끄적 > 자체 체형관련 끄적끄적' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Abdominal Gripping Syndrome Part 2 (0) | 2023.07.23 |
|---|---|
| Abdominal Gripping Syndrome Part 1. (0) | 2023.07.22 |
| 경추 스트레칭 (Neck stretching) 의 "허와 실" (1) | 2023.07.12 |
| 통증관련 딜레마( Dilemma)----일상생활부터 체크하라 두번째 해부생리학적 접근 (0) | 2023.07.10 |
| 통증관련 딜레마( Dilemma)----일상생활부터 체크하라 첫번째 (0) | 2023.07.09 |



